Explaining OSPF LSA(Link State Advertisement)
Guyz we have already learned what is OSPF in my previous post just in case you haven't here is the link(OSPF), because to learn OSPF LSA(Link State Advertisement) you need to know OSPF. Also, before we start with LSA we need to know some important OSPF terminologies.
Explaining OSPF Terminologies To Understand LSA(Link State Advertisement).
Here are the two important terms you need to know before understanding OSPF LSA:-
Link- A link can be a physical component or logical component. A physical link is like a router interfaces or nodes that provides a connection between two devices(routers) and when the link is used to connect to networks and has been assigned an IP address then that is a logical link.
Topological Database- The information in the LSA packets that are received from the routers in an area is stored in the Topological database in the form tables. These formations from the topological database are used by the router to input it into Dijkstra algorithm for calculating the shortest path to the remote network. Also, the link state advertisements are used to maintain and update the topological database.
LSA Flooding- OSPF uses this method to distribute routing information via link-state updates(LSU) packets that contain the link status so that all the OSPF routers have the same topology map.
Designated Routers- When OSPF routers are connected to the same broadcast networks, then an election is done on the basis of priority level and the one having the highest priority is selected as a designated router, also referred as DR and the objective of DR is to minimize the number of adjacencies formed and also, it is used to distribute the received routing information to the remaining routers and from the remaining routers on the broadcast network or link.
Backup Designated Router- As the name suggests, it is a backup or a hot standby for DR. Though BDR gets all the routing information from the OSPF adjacent routers but it will not disperse the LSA updates like DR does. But when the DR is down BDR will start giving the routing updates.
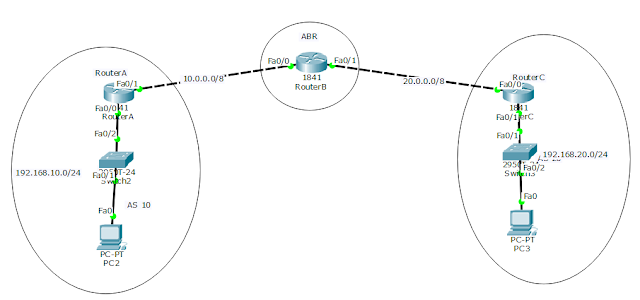
Area Border Router(ABR)- ABR concept is used when the routers are in two different areas ie in multi-area OSPF configuration. ABR routers are those routers that are at the border between an OSPF area and a backbone area(area 0). So In simpler terms, ABR is the member of both an OSPF area and the backbone area.
Autonomous System Boundary Router(ASBR)- ASBR concept is used to bring the connectivity between routers in an OSPF domain and routers running different routing protocol by using Autonomous System. So basically ASBRs are those routers that are members of both OSPF as well as the other routing protocol
Now getting back to our main topic of discussion, what is OSPF LSA(Link State Advertisements).
What Is (LSA)Link State Advertisement?
We are already aware that unlike Eigrp and RIP that uses routing by rumor, OSPF does routing by intelligence. Why intelligence because OSPF keeps track and keeps verifying the status of the links within their respective areas. The link status is stored in the LSA and if by chance a link is down, then the OSPF has to recalculate the whole route by rerunning the SPF algorithm, which consumes CPU.
In Simpler terms, an LSA(Link State Advertisement) is OSPF data packet that contains the link status and the routing information taken from the neighbor of all the routers in an area. Also, one important thing I must tell you is that an OSPF will only exchange LSA packets with a router to which it has form adjacencies.
Now let's talk about what are the different types of OSPF LSA(Link State Advertisements).
What Are The Types Of LSA(Link State Advertisement)?
There are 5 types of OSPF LSA(Link State Advertisement) and each type has an important role to perform in propagating routing information.
- Type 1(Router LSA)- All the links that are local to a router along with their status and the cost of those links are listed in Type 1 LSA. All the OSPF routers generate this LSA and then it is flooded to all the routers within the same area.
- Type 2(Network LSA)- This Type of LSA is generated by the designated router(DR) which contains the list of all the routers attached to it.
- Type 3(Network Summary link LSA)- This type of LSA is generated at an area by ABR and then they forward it to the other OSPF areas connected to the backbone area, so unlike Type 1 and Type 2, this LSA crosses boundaries and carry information send by one ABR at one end to other ABR at the other end of the boundary via backbone area. These LSAs contain a summary of network and link of the OSPF area along with the IP address and RID of the ABR that is generating and advertising the Type 3 LSA.
- Type 4(ASBR Summary LSA)- This type of LSA is generated by ABRs and then they forward this to the area external to the one in which they were generated much like how is done in LSA Type 3, but there is a big difference and that is, this type LSA is specifically used to inform the rest of the OSPF areas how to get to ASBRs.
- Type 5(AS External Link LSA)- This LSA is generated and advertised by ASBRs that contains the information of the routes external to the OSPF and are flooded everywhere. A type 5 LSA is generated for each individual external network that ASBR advertises.
Also Read This Hot Topic:- What Is OSPF?
Also Read This Hot Topic:- Eigrp Vs OSPF
So, guys, this is the end of my explanation for the topic what is OSPF LSA(Link State Advertisement). I have explained this complicated topic at the best of my capabilities, so if you'll like my explanation please share it and follow me on facebook or google plus for more. Also If you have any questions or doubts please comment it down below. See you guyz soon...
- Type 1(Router LSA)- All the links that are local to a router along with their status and the cost of those links are listed in Type 1 LSA. All the OSPF routers generate this LSA and then it is flooded to all the routers within the same area.
- Type 2(Network LSA)- This Type of LSA is generated by the designated router(DR) which contains the list of all the routers attached to it.
- Type 3(Network Summary link LSA)- This type of LSA is generated at an area by ABR and then they forward it to the other OSPF areas connected to the backbone area, so unlike Type 1 and Type 2, this LSA crosses boundaries and carry information send by one ABR at one end to other ABR at the other end of the boundary via backbone area. These LSAs contain a summary of network and link of the OSPF area along with the IP address and RID of the ABR that is generating and advertising the Type 3 LSA.
- Type 4(ASBR Summary LSA)- This type of LSA is generated by ABRs and then they forward this to the area external to the one in which they were generated much like how is done in LSA Type 3, but there is a big difference and that is, this type LSA is specifically used to inform the rest of the OSPF areas how to get to ASBRs.
- Type 5(AS External Link LSA)- This LSA is generated and advertised by ASBRs that contains the information of the routes external to the OSPF and are flooded everywhere. A type 5 LSA is generated for each individual external network that ASBR advertises.
Also Read This Hot Topic:- What Is OSPF?
Also Read This Hot Topic:- Eigrp Vs OSPF
So, guys, this is the end of my explanation for the topic what is OSPF LSA(Link State Advertisement). I have explained this complicated topic at the best of my capabilities, so if you'll like my explanation please share it and follow me on facebook or google plus for more. Also If you have any questions or doubts please comment it down below. See you guyz soon...